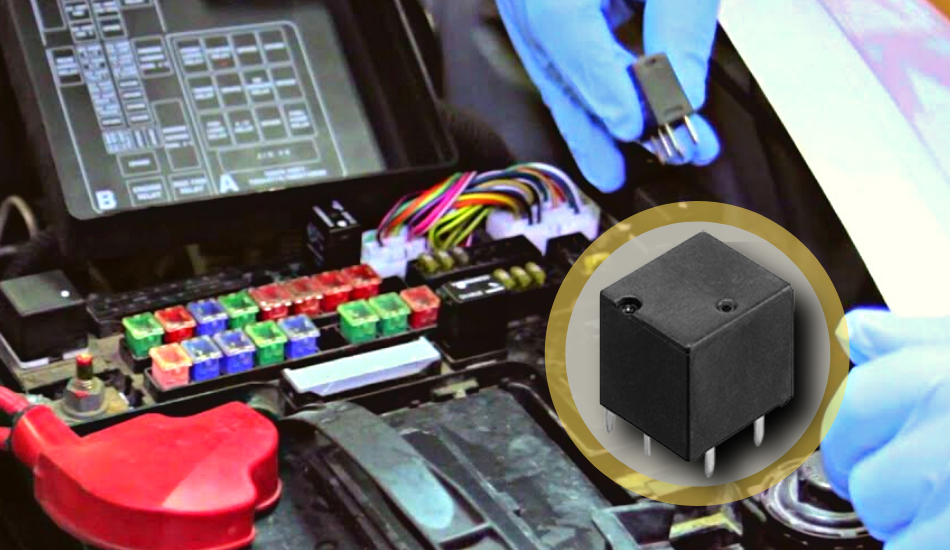
The Automotive Relay/Car Relay is a very small component in an automobile that saves lives. It is a very small and portable component of many bigger appliances in automotive vehicles.
To answer “what is the purpose of a relay in a car” we need to put a clear definition of automotive relays.
An Automotive Relay is a digital or electromechanical managed switch and it is designed for DC voltages in passenger consolation and retainment systems. It also controls power levels in harsh environments.
Generally, Car relays are an electric-powered switch that works with electromagnetism to transform small electric stimuli into large currents. This conversion takes place while an electrical current turns on electromagnets to shape or change the current circuits.
Leveraging vulnerable inputs to power more potent current, relays can efficiently act as a switch or an amplifier for the electrical current. These rely upon the favored applications.
How Do Automotive Relays Work?
Relays are switches managed via means of electric power, like any other switch, computer, or power module.
The reason for Automotive Relays is to automate this power to interchange electric circuits on and off at different instances. However, the actual advantage at the back of a relay is more than simply automation; additionally, they offer the capacity to interchange a couple of circuits, inclusive of exceptional voltage kinds, in the identical relay at an identical time. Now the question comes how many relays are in a car?
How Many Car Relays are in a Car?
The number of Car relays in a vehicle may depend on the features that are added to the vehicle and The 12VDC relays are the quality answer for complete voltage applications, as they permit a low current to go with the driver circuit to manage an excessive current to go with the drift circuit, like a vehicle’s horn, headlights, auxiliary lamps, fan automobiles, blower automobiles and limitless portions of device current on automobiles today.
Best Offer Available
What are the uses of a relay in the car?
Relays are frequently utilized in circuits to lessen the current that flows via the number one control switch. An enormously low amperage switch, timer, or sensor may be used to show a miles better potential relay on and stale. Another number one use for relays is while upgrading to halogen headlights on an older car.
The current draw for halogens is an awful lot more than the OEM headlight switches have been designed to carry, thereby setting extra pressure on the headlight switch. This can cause the untimely failure of the switch. Another required use for relays is while you’re putting in an electric-powered cooling fan. If you twine directly, without a relay, all the extra strain from the fan can be positioned at the switch, mainly once more to early failure.
What is the switching level of current in Automotive Relays
The most common conditions that require using a car relay happen while software desires to interchange from excessive to low current (or vice versa) in a similar circuit.
For example, the temperature sensors that power HVAC devices require a level of amperage that massively exceeds the potential in their wiring. Relays offer the important amplification to transform a small current into a bigger one.
How does the wiring of a relay work?
Best Offer Available
Relays range of their size, potential, and corresponding makes use of. However, even though they’ll range in those respects, all relays feature in basically the identical way: one circuit is used to power any other.
The unique way wherein this happens relies upon whether or not the relay is normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC).
Normally Open Relays
Most relays are normally open; this is, the second one, the large circuit is in the off role by the means of default.
In a normally open relay, power flows via an enter circuit, activating an electromagnet. This generates a magnetic subject that draws a touch to enroll in the second one. A large circuit permits the current to go with the drift. When the supply of power is removed, a spring attracts. The touch is far from the second circuit, preventing the go with the drift of energy and turning off the give-up device.
Normally Closed Relays
The basics of an NC relay are similar to an NO relay: there are circuits, with the second one being large, and an electromagnet moves a bodily touch among positions.
But in the case of an NC relay, the default states are reversed. When the primary circuit is activated, the electromagnet attracts the touch far from the second circuit. As such, NC relays hold the bigger circuit via means of default.
Components of Automotive Relays
All relays have identical number one additives however a few types can also additionally incorporate extra components relying on their functions on applications. Below are the most important additives as a way to be located on all varieties of relays:
- Frame – is a field or heavy-obligation body that includes and helps the numerous components of the relay.
- Coil – is a twine wound around a metallic core. It’s the component that causes an electromagnetic subject
- Armature – is a switching component that opens and closes the contacts. There is a connected spring that returns the armature to its authentic role.
- Contacts – it’s the carrying out of a component that causes the relay to make (close) or break (open) a circuit.
Relays have circuits; energizing circuits and contact circuits. The energizing facet has the coil even as the relay contacts have the touch faucet. A relay coil is energized while the current goes with the drift via the coil and creates a magnetic subject. In an AC unit, the polarity modifications are one hundred twenty instances. In keeping with the second, polarity is likewise constant in a DC system.
Conclusion
A relay is no more than remote switches that make use of an electromagnet to shut a contact point. When the relay magnet is provided with voltage, the factors contact and battery voltage are routed via the principal circuit.